Gear Head Wireless Keyboard Kb 3750 Software Download Updated FREE
Gear Head Wireless Keyboard Kb 3750 Software Download
Smart Install Overview
- Introduction
- Restrictions for Smart Install
- DHCP and Smart Install
- Adding a Client Switch to the Network
- Bankroll Up the Client Configuration
- Updating Client Switches
- Connecting to a Client Switch
Introduction
Smart Install is a plug-and-play configuration and image-direction feature that provides nada-touch deployment for new switches. You lot can ship a switch to a location, place information technology in the network and power it on with no configuration required on the device.
A network using Smart Install includes a grouping of networking devices, known as clients, that are served by a common Layer 3 switch or router that acts every bit a director. In a Smart Install network, you tin apply the Nix-Affect Installation process to install new access layer switches into the network without any assist from the network ambassador. The director provides a single direction point for images and configuration of customer switches. When a client switch is first installed into the network, the director automatically detects the new switch, and identifies the right Cisco IOS image and the configuration file for downloading. Information technology can allocate an IP address and host proper name to a client. If a standalone switch in the network is replaced by another switch of the same SKU (a switch with the same product ID), it automatically gets the same configuration and image equally the previous 1. The managing director tin can also perform on-need configuration and software prototype updates of a switch or a group of switches in the network.
Zero-bear upon updates also have place on preconfigured switches after you accept entered the write erase and reload privileged EXEC commands to clear the configuration.

The director tin can human activity equally a DHCP and TFTP server and can store the configuration and image files. These files can also be stored on a third-party TFTP server for the director to use. The customer can download the image and configuration files from the director TFTP server or from a remote server.

Note ![]() Switches running releases earlier than 12.2(52)SE are non Smart Install capable, but they tin can be Smart Install clients if they support the archive download-sw privileged EXEC command. Smart Install clients can be Layer 2 or Layer iii switches. Switches running Cisco IOS Releases 3.two(0)SE and afterward, and 15.0 (2)SE and later, 3.6.(0)Due east, and 15.ii.(ii)East back up Smart Install.
Switches running releases earlier than 12.2(52)SE are non Smart Install capable, but they tin can be Smart Install clients if they support the archive download-sw privileged EXEC command. Smart Install clients can be Layer 2 or Layer iii switches. Switches running Cisco IOS Releases 3.two(0)SE and afterward, and 15.0 (2)SE and later, 3.6.(0)Due east, and 15.ii.(ii)East back up Smart Install.
See Appendix A, "Supported Devices for Smart Install" for a listing of supported routers and switches, the roles they tin play (client or director), and the required software releases.
In a typical Smart Install network, a client switch uses DHCP to become an IP address and the director snoops DHCP messages. For a customer to participate in Smart Install zero-impact update, information technology must utilize DHCP, and all DHCP communication must pass through the manager so that it can snoop all DHCP packets from clients. The most automatic operation is when all switches in the Smart Install network use DHCP and are Smart Install capable. However, any client switch that supports the archive download-sw privileged EXEC command to download a software image can exist used in a nothing-touch Smart Install network. Cisco IOS Release 3.2(0)SE and later, support software install.

Note ![]() A Smart Install network tin can take simply i director.
A Smart Install network tin can take simply i director.
A client switch can participate in Smart Install even if it is not directly connected to the manager. The Smart Install network supports up to vii hops. Intermediate switches or clients continued to the director through an intermediate switch in a multihop environment tin be, only are not necessarily Smart Install-capable, provided the management VLAN is set to default VLAN1.
If you apply a VLAN other than vlan 1 for management, and so the intermediate switch must be Smart Install capable switch.
Figure i-1 shows a Smart Install network with external DHCP and TFTP servers. There can be only one director amongst TFTP servers in any Smart Install network. The director tin can also serve as the DHCP and TFTP server.
Figure ane-1 Typical Smart Install Network Diagram
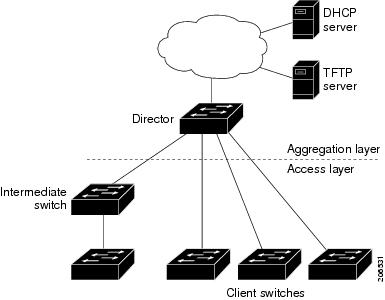
A Smart Install network can be:
- A network where all client switches are of the same product ID (PID), for instance, WS-2960S-48FPS-L. In this case, you lot tin identify a default image and a seed or basic configuration to apply on all client switches.
- A network that includes switches with different PIDs. In these networks, you tin configure switch groups and specify that the same images and seed configuration files are practical to all switches in the group. A group can exist based on a predefined PID, or yous tin create groups based on product ID, MAC address, switch stack number, MAC accost, or customer switch connectivity to a specific upstream neighbor. When switches in a group are replaced by another switch with the same product ID, the replacement switch receives the same configuration and image.
After a switch has an image and bones configuration, you lot tin can configure specific features on individual switches and salvage the configuration to the startup configuration file.
Switches participating in Smart Install nil-impact updates must apply DHCP to obtain their IP addresses. DHCP options are used to send:
- Image filename and location
- TFTP server IP accost
- Hostname
- Configuration filename
- Managing director IP address to the other switches
When a director is configured and a customer joins the Smart Install network, Smart Install is automatically enabled on these devices. Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 12.ii(58)SE, XE three.4SG, 15.1(2)SG, 15.1(ane)SY, xv.0(two)SE, iii.two(0)SE and later, 3.vi.(0)E, or 15.2.(two)E, y'all can disable Smart Install on a device and besides shut down its Smart Install TCP ports by entering the no vstack global configuration control on the client or manager. When Smart Install is disabled on a device, any Smart Install configuration on it remains in the running configuration but does non take effect while Smart Install is disabled. To reenable Smart Install on the device, enter the vstack global configuration control.
These sections include more than detailed information on Smart Install components:
- Smart Install Director
- Smart Install Clients
- Smart Install Groups
Smart Install Director
The director in a Smart Install network must be a Layer three switch running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(52)SE or later on, XE 3.4SG, 15.1(ii)SG, fifteen.0(2)SE or after, 15.1(1)SY or later, three.ii(0)SE or subsequently, or a router running Cisco IOS Release 15.1(3)T or later. Run into Appendix A, "Supported Devices for Smart Install" for a list of routers and switches that can perform the role of Smart Install manager.

Note ![]() IE2000 IE3000, and IE3010 back up Managing director with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(two)E.
IE2000 IE3000, and IE3010 back up Managing director with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(two)E.
To configure a device as director, enter the IP address of 1 of its Layer three interfaces in the vstack director ip_ address global configuration control and enable it as director past entering the vstack bones command.

Annotation ![]() If yous have entered the no vstack global configuration command to disable Smart Install on a device, the vstack director ip_ address and vstack basic global configuration commands are non immune on the device. To reenable Smart Install on a device, enter the vstack global configuration command.
If yous have entered the no vstack global configuration command to disable Smart Install on a device, the vstack director ip_ address and vstack basic global configuration commands are non immune on the device. To reenable Smart Install on a device, enter the vstack global configuration command.
When a device is configured as manager, The VLAN on which the DHCP snooping is automatically enabled becomes VLAN ane past default. The director begins building the director database in VLAN i. To specify another VLAN for Smart Install management, you can use the vstack startup-vlan global configuration command. Depending on the VLAN that is specified in the command, DHCP snooping is enabled on that VLAN so that the director can identify new switches that are connected to the network, known as not-VLAN one switches.
The database lists the client devices in the Smart Install network and includes this information:
- Type of switch (PID) for all switches, including switches in a stack
- MAC addresses for all switches, including switches in a stack
- IP address of the switch or stack
- Hostname
- Network topology including neighbors interfacing with the switch
- Serial number (but Smart Install capable switches)

Note ![]() When the director is a switch, DHCP snooping is enabled on VLAN 1 by default. It is also enabled on other Smart Install direction VLANs that are configured by entering the vstack vlan vlan-range global configuration command. Y'all can utilize the vstack startup-vlan global configuration control to specify another VLAN that should be used for Smart Install management. Cisco IOS Releases 15.1(ane)SY, 15.0(ii)SE or subsequently, 15.ane(2)SG, three.6.(0)Eastward, fifteen.2.(2)Eastward, and Cisco IOS XE 3.4SG support non-VLAN1 direction and provide the ability to discover the client switches bachelor on non-VLAN1.
When the director is a switch, DHCP snooping is enabled on VLAN 1 by default. It is also enabled on other Smart Install direction VLANs that are configured by entering the vstack vlan vlan-range global configuration command. Y'all can utilize the vstack startup-vlan global configuration control to specify another VLAN that should be used for Smart Install management. Cisco IOS Releases 15.1(ane)SY, 15.0(ii)SE or subsequently, 15.ane(2)SG, three.6.(0)Eastward, fifteen.2.(2)Eastward, and Cisco IOS XE 3.4SG support non-VLAN1 direction and provide the ability to discover the client switches bachelor on non-VLAN1.
In a Smart Install network that uses DHCP to assign IP addresses, yous just need to configure the director. Client switches do not require any configuration. Although yous can enter command-line interface commands on clients, configuration commands do not have effect unless the switch assumes the function of director.

Note ![]() You can configure the vstack commands in client style. only this is effective just when the switch is converted to a manager.
You can configure the vstack commands in client style. only this is effective just when the switch is converted to a manager.
At that place tin can exist merely one director for a set up of clients and you cannot configure a backup managing director. If the manager fails:
- Director database must be rebuilt.
- Any update being performed for a non-Smart Install-capable switch might fail.
- The accumulated download status is lost.
- A configuration backup might not occur earlier the managing director restarts.
The director can change status and get a customer switch if:
- The director interface that has the managing director IP address shuts down.
- The director interface that has the director IP accost is deleted.
- The manager IP accost is changed.
If the director becomes a client, DHCP snooping is disabled, and the managing director database is no longer used.
If the director IP accost is provided by DHCP and you configure a different director IP address on a client switch, the client is longer function of the director'south Smart Install network.
Smart Install relies on a TFTP server to store paradigm and configuration files. The TFTP server can be an external device, or the director can act as a TFTP server. If the director is the TFTP server, the available flash file space on the manager must be adequate to accommodate the client Cisco IOS image and configuration files. See the "Configuring the TFTP Server" section.
In a Smart Install network using DHCP, the DHCP server can be an external device or the managing director can act every bit the DHCP server. Run into the "Configuring the DHCP Server" department. The director snoops all DHCP packets that pass through it on VLANs that are configured as Smart Install management VLANs. All network DHCP packets from intermediate or client switches or from an external DHCP server must pass through the director. The managing director must be able to snoop all DHCP packets from clients.

Note ![]() Smart Install options in the DCHP offering are choice 125, suboption 5 (the image list file), option 125 sub-pick xvi (the director IP address), and pick 67 (the configuration file).
Smart Install options in the DCHP offering are choice 125, suboption 5 (the image list file), option 125 sub-pick xvi (the director IP address), and pick 67 (the configuration file).
The director builds a topology director database for the network by collecting information from the network Smart Install switches. The director uses the database:
- To assign a configuration file and epitome to a customer.
- As a reference to obtain the PID, the image proper noun, and the configuration file for an on-need update of network switches.
The director periodically updates the manager database based on CDP updates that information technology receives from neighbor switches and from Smart Install messages sent to the director by Smart Install capable clients. The updates contain information most the client neighbors.
Image List File
An paradigm list identifies the images to be loaded on the client. The paradigm listing file is the file that contains the correct prototype name for the customer. When the director is the TFTP server, this file is stored in flash memory. Otherwise, it is stored in a remote, 3rd-political party TFTP server.
- When the file is stored in the managing director, the prefix for the image list is flash: //, usbflash0: //, bootflash://, bootdisk://, or disk0:// based on the advisable file systems available on the switch.
- When the file is stored in a remote TFTP server, the prefix is tftp: // ip_address / paradigm. tar.

Annotation ![]() In Goad Switches 3850 and 3650, the prototype is a arranged with .bin extension.
In Goad Switches 3850 and 3650, the prototype is a arranged with .bin extension.
Images must be stored either on the managing director or on the third-party TFTP server.
For a standalone switch, the image listing file contains a single image. For a stack, the image list contains images for all members of the stack, which could be the same epitome or different images. For a switch stack, the manager creates the paradigm list file subsequently the user specifies the tar file for each switch in the stack.
Starting with Cisco IOS Release 12.two(55)SE or subsequently,15.1(1)SY, 15.0(ii)SE and later, 3.2(0)SE and later, XE three.4SG, fifteen.1(2)SG, iii.half-dozen.(0)E, and 15.ii.(2)E, when the user specifies the tar file for each switch, the manager automatically creates the imagelist file.
When an external TFTP server is used, the director writes the image listing file to the TFTP server. It is recommended that the TFTP server permit the manager to write the image listing files to the TFTP Server. If the manager does not have permission to write to the file organization of the TFTP server, the manager logs the failure in the organization log. Y'all tin can create the image list files and put them on the TFTP server manually if the managing director fails to do and then automatically; you cannot prepare the result that prevents the managing director from writing to the TFTP server.

Note ![]() The upgrade process is initialized fifty-fifty when the imagelist file is copied manually, but the director tries to copy the image list file to the TFTP server and the failure arrangement log is displayed periodically.
The upgrade process is initialized fifty-fifty when the imagelist file is copied manually, but the director tries to copy the image list file to the TFTP server and the failure arrangement log is displayed periodically.
Configuration Files
The director manages these configuration files:
- Startup configuration—The configuration that a client uses when it boots.
- Seed configuration—A configuration on the director that is the basis for the client startup configuration.
- Backup configuration—An exact copy of a customer startup configuration stored in the director.
Smart Install Clients
Client switches accept a straight or indirect connection to the managing director and then that they tin can receive epitome and configuration downloads from it. A switch becomes a Smart Install client when either director or when the director IP accost is configured on the switch manually. Client switches use the managing director database for image and configuration downloads and receive the image and configuration files from the Smart Install TFTP server.
A client switch tin can be an intermediate switch connected to another client switch. A customer can exist a standalone switch or a switch stack.
- Director can download images and configuration of clients that are not Smart Install. However, such clients are entered into the director database only if they are connected to a Smart Install capable switch. The director tin telnet to the client switch and utilise the archive download-sw privileged EXEC command to download software to the switch. The director must know the client switch password to perform the download.
- Smart Install capable switches can communicate directly with the director to update switch information, can have images and configuration downloaded, and tin be managed by the director. A Smart Install capable customer with the director IP address and connectivity to the director sends switch and neighbor information to the managing director by using the Smart Install protocol.

Notation ![]() Switches running Cisco IOS XE Releases three.2(0)SE and later, three.6.(0)E, and 15.2.(ii)E support software install.
Switches running Cisco IOS XE Releases three.2(0)SE and later, three.6.(0)E, and 15.2.(ii)E support software install.
All switches in the network with "network" connectivity to the director can be clients, whether or non they are Smart Install capable. A client switch needs an IP address for management communication and the director must be able to communicate with that IP address. Client switch IP addresses are assigned past DHCP or statically configured.
Smart Install capable clients transport switch and neighbor information to the continued director for the managing director database. Client switches that are not Smart Install capable or that are not connected to a Smart Install capable switch are not entered into the director database. In a multihop topology, for the director to become the complete topology overview, whatever customer switch upstream of a group of clients must be Smart Install capable. Clients not in the director database tin can get an on-need update, but they cannot get a aught-affect or group update.
Figure one-two shows some possible means that clients tin can be interconnected in a network. Table i-i and Tabular array 1-2 shows the director database knowledge of each client and the type of update that is supported.

Annotation ![]() The topology shown in Figure one-2 does not represent a typical Smart Install topology only is used to demonstrate possible types of client interconnections.
The topology shown in Figure one-2 does not represent a typical Smart Install topology only is used to demonstrate possible types of client interconnections.
Effigy 1-2 Possible Interconnections of Smart Install Clients
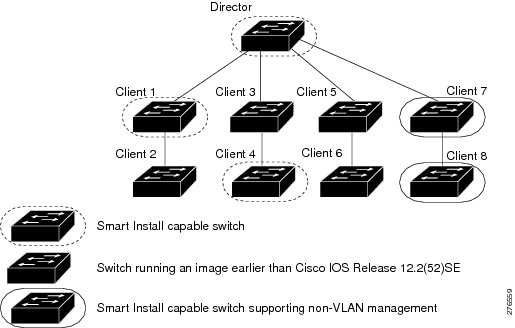

Notation ![]() The Cisco IOS releases12.2(52)SE or later on, XE 3.4SG, 15.1(ii)SG, 15.1(1)SY and after, 15.0(2)SE and afterward, and 3.2(0)SE and afterwards, support the director role. The Cisco IOS releases fifteen.0(two)SE, 15.1(1)SY, 15.1(two)SG, XE three.4SG, xv.0(2)EX, 15.0(2)EX1, 3.vi.(0)East, and 15.2.(ii)East are Smart Install capable switches, supporting not-VLAN 1 management and providing the ability to discover the customer switches bachelor on non-VLAN 1.
The Cisco IOS releases12.2(52)SE or later on, XE 3.4SG, 15.1(ii)SG, 15.1(1)SY and after, 15.0(2)SE and afterward, and 3.2(0)SE and afterwards, support the director role. The Cisco IOS releases fifteen.0(two)SE, 15.1(1)SY, 15.1(two)SG, XE three.4SG, xv.0(2)EX, 15.0(2)EX1, 3.vi.(0)East, and 15.2.(ii)East are Smart Install capable switches, supporting not-VLAN 1 management and providing the ability to discover the customer switches bachelor on non-VLAN 1.
Table 1-1 shows the switches that are in the managing director database and how the managing director obtained the data. When a client is a single hop from the director, the client uses CDP to send the managing director information most itself. When a customer is a Smart Install capable switch, it sends information to the director near itself and its neighbors.
| | | |
|---|---|---|
| Customer 1 | Yes | Learned from CDP and from Smart Install. The client also sends information about its neighbour (Client 2). |
| Customer 2 | Aye | Information received from Client 1. |
| Client 3 | Yes | Learned from CDP. |
| Customer four | No | No information available. The client is not an immediate neighbor of the managing director or another Smart Install switch. |
| Client 5 | Yes | Learned from CDP. |
| Client half dozen | No | No information available. The customer is not an firsthand neighbor of the director or another Smart Install switch. |
| Client 7 | Yes | Learned from CDP and from Smart Install. The client too sends information nigh its neighbor Client 8. Client 7 is a non-VLAN 1 switch. |
| Client 8 | Yes | The information to Client 8 volition be sent by Client seven via non-VLAN1. Client 8 is a non-VLAN 1 switch. |
Tabular array 1-2 shows the managing director database knowledge of each client and the type of update that is supported in various software versions. For information near Smart Install supported switches, routers, and minimum software releases for directors and clients, come across Supported Devices for Smart Install .
| | | | | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client 1 | 12.two(52)SE or afterward | Yes | Yeah | Yes |
| Client 2 | Earlier than 12.two(52)SE | Yes | Yes | Yeah |
| Customer three | Earlier than 12.ii(52)SE | Yes | Aye | Yes |
| Client four | 12.2(52)SE or afterward | Yes | Yep | Yes |
| Client 5 | Before than 12.2(52)SE | Yeah | Yes | Yep |
| Client half-dozen | Earlier than 12.2(52)SE | Yes | Yes | No. Switch not in director database. |
| Client seven | 15.0(2)SE, xv.one(1)SY, xv.one(2)SG, XE 3.4SG, xv.0(2)EX, xv.0(2)EX1, 3.6.(0)E, and fifteen.2.(two)E | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Client 8 | 15.0(ii)SE,15.1(1)SY, 15.1(2)SG, XE three.4SG, fifteen.0(ii)EX, 15.0(two)EX1, three.vi.(0)E, and 15.ii.(2)E | Yes | Aye | Yes |
To encounter the types of Smart Install clients in a network, enter the bear witness vstack condition privileged EXEC command.
These fields were added in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(58)SE or fifteen.1(1)SY to provide more information about each client:
- Device type: South (Smart Install capable, running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(52)SE or afterwards, 15.one(one)SY, xv.0(2)SE and later, 3.2(0)SE and later), 3.6.(0)Due east, or 15.2.(ii)E, North (non a Smart Install device), or P (pending, unable to decide).
- Device health condition: Active (the director is receiving periodic updates from the device) or Inactive (the device is disconnected or has not provided updates for three consecutive keepalive periods)
- Join window status: a (allowed), h (on concur), or d (denied). Run into the "Using a Join Window" section.
- Upgrade condition: An image update is i (in progress), I (consummate), or X (failed). A configuration upgrade is c (in progress), C (complete), or 10 (failed).
Smart Install Groups
When all switches in a Smart Install network have the aforementioned PID, they tin run the same prototype and the same seed (basic) configuration file. In this case, you lot can assign a default image and configuration file for all clients. Nevertheless, if there is more than than one PID in the network or if you want a different configuration file to run on some switches, depending on their role in the network, you lot should configure Smart Install groups and assign an epitome and configuration file for each group.
- Custom groups take precedence over congenital-in groups and are based on:
–![]() Stack grouping—For switches in a stack, you can configure groups based on their number in the stack. Stack groups are used only for switch stack upgrades, and clients do non demand to be in the director database. Starting with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(58)SE, 15.1(i)SY, fifteen.0(2)SE and later, 3.two(0)SE and after, three.6.(0)East, and 15.two.(two)E if a stack is homogeneous (all one switch blazon), you do non need to place each switch type.
Stack grouping—For switches in a stack, you can configure groups based on their number in the stack. Stack groups are used only for switch stack upgrades, and clients do non demand to be in the director database. Starting with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(58)SE, 15.1(i)SY, fifteen.0(2)SE and later, 3.two(0)SE and after, three.6.(0)East, and 15.two.(two)E if a stack is homogeneous (all one switch blazon), you do non need to place each switch type.
–![]() MAC address—Y'all tin can create a custom grouping of specific switches by using the MAC addresses of the switches to configure the group. You lot can include switches with the same or different production IDs, every bit long as they use the same image and configuration file. Enter the prove vstack neighbors all privileged EXEC control to run across the MAC addresses of switches in the Smart Install network.
MAC address—Y'all tin can create a custom grouping of specific switches by using the MAC addresses of the switches to configure the group. You lot can include switches with the same or different production IDs, every bit long as they use the same image and configuration file. Enter the prove vstack neighbors all privileged EXEC control to run across the MAC addresses of switches in the Smart Install network.
–![]() Connectivity—You can configure a custom group based on network topology; that is, all switches that have the same upstream neighbor. Connectivity groups take precedence over groups with matching product IDs or stack numbers. Connectivity groups include only standalone switches (non switch stacks), and clients must be in the managing director database.
Connectivity—You can configure a custom group based on network topology; that is, all switches that have the same upstream neighbor. Connectivity groups take precedence over groups with matching product IDs or stack numbers. Connectivity groups include only standalone switches (non switch stacks), and clients must be in the managing director database.
–![]() Product IDs (PIDs)—These product IDs are all supported models, including newer PIDs that were not shipping when the software was released and therefore are non in the CLI. PID groups include only standalone switches (non switch stacks), and clients exercise not need to be in the director database.
Product IDs (PIDs)—These product IDs are all supported models, including newer PIDs that were not shipping when the software was released and therefore are non in the CLI. PID groups include only standalone switches (non switch stacks), and clients exercise not need to be in the director database.
The priority of custom groups from high to low is stack group, MAC address, connectivity, and product ID.
- Built-in groups are based on PIDs that yous tin select from the CLI. These stand for the fixed Ethernet switching products that were shipping when the software was released, for case, 3750, 3560, 2975, 2960, 3850, and 3650.
Switches that belong to a grouping apply the image and configuration file assigned to that group. If a customer switch does not belong to a group in the director database, it is assigned the default image and configuration file.

Note ![]() If there is more than than ane switch PID in the network, we recommend configuring congenital-in or custom groups. The default image and configuration is used in networks with only one product ID.
If there is more than than ane switch PID in the network, we recommend configuring congenital-in or custom groups. The default image and configuration is used in networks with only one product ID.
An example of the use of custom groups is a network where all client switches are the same PID, but one requires a different configuration. For example, a retail store might have checkout counters and a chemist's shop, and the pharmacy switch requires a different configuration. The checkout counters would utilize the default configuration, but you lot would create a custom group for the pharmacy.
Restrictions for Smart Install
The absence of an authorization or authentication mechanism in the Smart Install protocol betwixt the customer and the director can allow a customer to process crafted Smart Install messages as if these messages were from the Smart Install Managing director. These include the post-obit:
- Change the TFTP server accost on Smart Install clients.
- Copy the startup configuration of client switches to the previously-changed and assailant-controlled TFTP server.
- Substitute the startup configuration of clients with a configuration created by the assaulter, and forcing a reload of the clients after a configured time interval.
- Upgrade the IOS image on client switches to an image supplied by the attacker.
- Execute arbitrary commands on client switches (applicable to Cisco IOS Release fifteen.two(2)Eastward and later releases and Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.0E and later releases.)
While designing a Smart Install architecture, intendance should exist taken such that the infrastructure IP address space is not accessible to untrusted parties. Design considerations are listed in the Security Best Practices section of this certificate.
Security Best Practices
Security best practices around the Cisco Smart Install feature depend on how the feature is used in a specific customer environment. We differentiate the post-obit use cases:
- Customers not using the Smart Install feature.
- Customers leveraging the Smart Install characteristic only for null-touch deployment.
- Customers leveraging the Smart Install feature for more than naught-touch deployment (configuration and image-direction).
The following sections depict each scenario in detail:
Customers Not Using the Smart Install Feature
Customers who do not utilize the Cisco Smart Install characteristic, and are running a release of Cisco IOS and IOS XE Software where the command is available, should disable the Smart Install feature with the no vstack command.

Notation ![]() The vstack command was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(55)SE03.
The vstack command was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(55)SE03.
The following is sample output from the show vstack command on a Cisco Catalyst Switch with the Smart Install client feature disabled:
switch# show vstack config Role: Client (SmartInstall disabled) Vstack Director IP address: 0.0.0.0 Customers Leveraging the Smart Install Feature Simply for Goose egg-Impact Deployment
Disable the Smart Install client functionality later on the zero-touch installation is complete or use the no vstack command.
To propagate the no vstack command into the network, use i of the following methods:
- Execute the no vstack command on all client switches either manually or using a script.
- Add the no vstack command as function of the IOS configuration that is pushed into each Smart Install client equally part of the null-touch installation.
- In the releases that practise not back up the vstack control (Cisco IOS Release 12.2(55)SE02 and prior releases), utilise an access control list (ACL) on client switches to block the traffic on TCP port 4786.
To enable the Smart Install customer functionality later on, execute the vstack command on all client switches either manually or by using a script.

Notation ![]() If the configuration changes in betwixt the disabling and re-enabling of the Smart Install feature, to preserve these changes, execute the write memory control on customer switches later re-enabling the feature. Configuring the command ensures a successful fill-in of the startup configuration of customer switches.
If the configuration changes in betwixt the disabling and re-enabling of the Smart Install feature, to preserve these changes, execute the write memory control on customer switches later re-enabling the feature. Configuring the command ensures a successful fill-in of the startup configuration of customer switches.
Customers Leveraging the Smart Install Feature for More than Than Zero-Bear on Deployment
While designing a Smart Install architecture, care should exist taken such that the infrastructure IP address space is not accessible to untrusted parties. In releases that do not support the vstack command, ensure that simply the Smart Install director has TCP connectivity to all Smart Install clients on port 4786.
Administrators can apply the post-obit security best practices for Cisco Smart Install deployments on affected devices:
- Interface access control lists (ACLs)
- Control Plane Policing (CoPP). This feature is not available in all Cisco IOS Software releases.
The following example shows an interface ACL with the Smart Install manager IP accost as 10.10.10.1 and the Smart Install client IP address as 10.10.10.200:
ip access-list extended SMI_HARDENING_LIST
permit tcp host 10.x.ten.one host ten.ten.ten.200 eq 4786
deny tcp any any eq 4786
permit ip whatever any
This ACL must be deployed on all IP interfaces on all clients. It can also be pushed via the managing director when switches are get-go deployed.
To further restrict admission to all the clients inside the infrastructure, administrators tin can use the post-obit security best practices on other devices in the network:
- Infrastructure access control lists (iACLs)
- VLAN admission control lists (VACLs)
Migration Plan
Customers who can non properly protect their Smart Install IP infrastructure accost space, or need the added security of authorization and authentication between the director and clients tin can migrate to Cisco Plug-N-Play (PnP). For more information, see the PnP Feature Guide.
If your release does not back up PnP, migrate to Smart Install Proxy (SMI Proxy). The SMI Proxy feature must be enabled on a network device that is configured every bit a PnP Agent. This device will bridge the communication between older devices running Smart Install and the PnP Server. The SMI Proxy device will contact the central PnP Server on behalf of the device running older versions, to recall the image and configuration information. For more than information, see the SMI Proxy affiliate.
SMI Proxy is bachelor in Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2)E2 and later releases.

Note ![]() The security best practices must be followed for all devices on which the SMI Proxy feature is enabled, and also for all devices on which the Smart Install characteristic is enabled.
The security best practices must be followed for all devices on which the SMI Proxy feature is enabled, and also for all devices on which the Smart Install characteristic is enabled.
DHCP and Smart Install
DHCP is recommended in Smart Install networks and is required for zero-bear upon updates. On-need updates practise non crave DHCP. In a DHCP network, DHCP snooping is automatically enabled on the director. The managing director snoops DHCP offers and requests to and from the customer switches and uses DHCP snooping to insert the DHCP options used in the Smart Install operation.
However, because DHCP snooping is not supported on routed ports, you lot should not connect routed ports directly to the client or the director.
A DHCP server in a Smart Install network tin be positioned in one of these means:
- The Smart Install director can act equally the DHCP server in the network. When the DHCP offer goes to the customer switches, the director allocates the IP addresses and assigns configurations and images and the hostname as DHCP options in the DHCP offer and DHCP acknowledgment. DHCP snooping is automatically turned on for the director.
- The DHCP server can be another device (third-political party server) in the Smart Install network. In this example, DHCP packets between the clients and DHCP server must pass through the director.

Note ![]() Y'all tin can configure a join-window time menses then that the director tin can only modify the DHCP offering and send the image and configuration files to the client during the configured window. The join window restricts Smart Install for a specified period of time and acts as a security precaution to control when a client can receive these files. Meet the "Using a Bring together Window" section.
Y'all tin can configure a join-window time menses then that the director tin can only modify the DHCP offering and send the image and configuration files to the client during the configured window. The join window restricts Smart Install for a specified period of time and acts as a security precaution to control when a client can receive these files. Meet the "Using a Bring together Window" section.
- A third-party server and the manager DHCP server can coexist in a network. In this case, the director is responsible just for the DHCP requests of the switches in the Smart Install network. The director maintains the Smart Install database and pool; other DHCP database functions are maintained past the third-party server.
Meet the "Configuring the DHCP Server" department for configuration instructions.
If the Smart Install DHCP server is the director or another device running Cisco IOS and the network reloads, the server might assign new IP addresses to participating switches. If a switch IP address changes, it might no longer be reachable. If the managing director IP address changes, information technology is no longer the Smart Install director, which could break the director and client switch relationships. This is an unlikely but possible corner-instance occurrence. To prevent this occurrence, y'all should enable DHCP remembering by entering the ip dhcp recollect global configuration command or the recall DHCP-puddle configuration command on the DHCP server,
Non-Cisco IOS third-party DHCP servers crave an IP-address-to-MAC-accost binding to ensure that the same IP accost is given to a switch on a reload.

Note ![]() In Smart Install networks that practice not use DHCP, you must manually configure the director IP address on each client switch by entering the vstack director ip-accost global configuration command. Client switches require only the director IP address. Smart Install networks that exercise non use DHCP cannot support zip-touch updates but can support on-demand update.
In Smart Install networks that practice not use DHCP, you must manually configure the director IP address on each client switch by entering the vstack director ip-accost global configuration command. Client switches require only the director IP address. Smart Install networks that exercise non use DHCP cannot support zip-touch updates but can support on-demand update.
Adding a Client Switch to the Network
When a switch arrives from the mill, it contains the factory default image. When it is plugged in and connected to the network and boots upwards, it tries to get its IP address from DHCP. When a device is added to the network, a notification is sent to the managing director that a new customer has joined. If the switch is connected (directly or indirectly) to the Smart Install manager, the manager recognizes the new switch through DHCP offers and acknowledgments. The managing director searches its database to determine if the switch belongs to a configured grouping. If non, the director determines if the switch matches the Smart Install network default PID. If the managing director has a configuration for the type of client that was added and if the join window is open up, the new customer receives the epitome and configuration files.

Note ![]() When clients in a Smart Install network consist of more than ane PID, you lot should configure congenital-in groups or custom groups based on MAC address, connectivity, stack group, or product-ID, and ascertain the image and configuration files for each group.
When clients in a Smart Install network consist of more than ane PID, you lot should configure congenital-in groups or custom groups based on MAC address, connectivity, stack group, or product-ID, and ascertain the image and configuration files for each group.
If the DHCP Server is external or internal (running on the director), the director inserts options into the DHCP response, informing the client where to download its IOS image and configuration file provided the join window is open.

Note ![]() If a bring together window has been configured, the Smart Install configuration and image files are sent to the client merely during the configured time period. A client switch sends an fault message if information technology cannot download an epitome or configuration file due to misconfiguration, if the epitome or configuration file is not available, or if a join window is configured and the DHCP acknowledgments occurs beyond the configured time frame. See the "Using a Join Window" section for more data.
If a bring together window has been configured, the Smart Install configuration and image files are sent to the client merely during the configured time period. A client switch sends an fault message if information technology cannot download an epitome or configuration file due to misconfiguration, if the epitome or configuration file is not available, or if a join window is configured and the DHCP acknowledgments occurs beyond the configured time frame. See the "Using a Join Window" section for more data.
Subsequently a switch has been added to the Smart Install network, you tin can do an on-need download of an epitome or configuration file to the client at any time if the switch meets these criteria:
- A switch that is non Smart Install capable must have an enable style password and a valid IP interface.
- A switch running the Smart Install paradigm must have a valid IP interface.
If a customer switch in the Smart-Install network is running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(55)SE or later, or 3.2(0)SE and subsequently, 15.0(two)EX, fifteen.0(2)EX1, 3.6.(0)E, and 15.two.(2)E is replaced with a switch with the same product ID, the new client receives the same image and configuration equally the replaced client. Se the "Replacing a Customer Switch" section.
See Affiliate 2, "Configuring Cisco Smart Install Devices" for typical configurations.
Backing Upwards the Client Configuration
Later on a client boots up, it sends a re-create of its startup configuration to the director. This file is the backup configuration for that client. Whatsoever time the user, directly or through the managing director, saves a client configuration, a backup configuration is created. The configuration is stored on the local repository on the manager or on a remote repository on a server. The backup file is used to reconfigure a customer during a zero-touch replacement.

Note ![]() Customer backup is supported just when the director and client are running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(55)SE or later on.
Customer backup is supported just when the director and client are running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(55)SE or later on.
Customer configuration fill-in is enabled by default. Yous can disable it by entering the no vstack fill-in global configuration command. You enable the file fill-in feature on the director by inbound the vstack backup and you can configure a repository for the backup files. If you do not specify a repository, the files are stored in the managing director flash:/vstack directory.
A customer configuration fill-in is triggered:
- When the write memory privileged EXEC control is entered on the customer.
- When the manager boots up, it requests configuration information from clients and backs up these configurations.
Replacing a Client Switch
You lot tin utilize zilch-touch replacement to exchange and install a like-type client in the Smart Install network. When a new switch is added to the network, a CDP database update is sent to the managing director, which determines if this is a new MAC address and therefore a new client. When a client needs to exist replaced and is removed from the network, the CDP database lists the removed customer every bit inactive. If some other client MAC address with the same product-ID is detected on the aforementioned port, this client is considered a replacement client. The director gives it the aforementioned image and configuration that the previous client had.
The director removes the entry for the replaced client from the manager database. If the replaced client is put elsewhere in the network, the director creates a new entry for it that includes the client's new data.
During a zip-touch replacement, the replacement client receives the final backed-upwardly configuration file, which is stored in the director or a remote repository. Customer configuration files are backed up by default, unless you disable this functionality on the manager.
Only 1 Smart Install client can exist replaced at a time on the same co-operative and only if there is 1 path to the managing director.

Notation ![]() Zip-bear upon replacement is supported only when the managing director and the replaced customer are running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(55)SE or later, fifteen.1(ane)SY, 15.0(2)SE and later, three.ii(0)SE and later, 15.0(2)EX, fifteen.0(ii)EX1, three.6.(0)E, or 15.2.(2)E. When a client switch running an earlier release is replaced, the new switch receives a seed replacement.
Zip-bear upon replacement is supported only when the managing director and the replaced customer are running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(55)SE or later, fifteen.1(ane)SY, 15.0(2)SE and later, three.ii(0)SE and later, 15.0(2)EX, fifteen.0(ii)EX1, three.6.(0)E, or 15.2.(2)E. When a client switch running an earlier release is replaced, the new switch receives a seed replacement.
When the replacement client and existing client do not take the same product ID, port connections, or interfaces, the replacement customer is considered new to the Smart Install network. For example, a replacement client must be connected to the same ports on the director and on other client switches as was the original client. When a new device is added to the network, a notification is sent to the managing director that a new customer has joined. If the director has a configuration for the type of client that was added and if the join window is open, the new client receives the image and configuration files.
Using a Bring together Window
A join window is a time window during which the client can update paradigm or configuration files. The manager can provide information nearly the image and configuration to the client only during this window. A client attempting to bring together the Smart Install network exterior the join window is not allowed to do so and cannot update the image and configuration files.
Employ the vstack join-window way automobile global configuration command to automatically update clients with the latest epitome and configuration files when they are added during a join window. Employ the no vstack bring together-window fashion global configuration command to put the client in a agree state.
Use the following commands to open or close a join window:
- Enter the vstack join-window commencement [date] hh:mm [interval] [end date] [recurring] global configuration command to configure a time window to command downloads of configuration and prototype files to customer switches.
- Enter the vstack bring together-window close global configuration command to manually close a join window, enter the no vstack join-window close global configuration control to manually open up a join window.

Note ![]() You cannot combine the vstack join-window kickoff and [no] vstack bring together-window commands to close and open the join window.
You cannot combine the vstack join-window kickoff and [no] vstack bring together-window commands to close and open the join window.
If a join window is configured, a zero affect update is possible simply during the configured window. If a switch connects to the managing director at whatever time other than during the bring together window, the Smart Install configuration and image files are not automatically downloaded. Instead, the new switch receives the default files from th e DHCP server. This feature provides control of the files and prevents unauthorized switches from receiving the Smart Install configuration.
If a bring together window is non configured, a zero touch update tin happen at any time considering that is the default state.
When a join window is configured, and the DHCP acknowledgement occurs outside of the configured window, a customer switch sends an error message that it cannot download an image or configuration file.
Configuring Join Window Mode
The bring together window way includes a hold state that adds an actress level of security for the client. The hold state lets you control whether or non the client can receive a software upgrade, and how the upgrade is performed. The hold-country is either on or off when the join window is active.
You configure automated join window mode with the vstack join-window mode auto global configuration command. In this style, when a customer joins the network, the director automatically upgrades it when the join window is open.
When you gear up the mode to manual by entering the no vstack join-window mode global configuration command, when a client joins the network during an open join window, the client is put on the hold list.
You tin can review clients on the hold list by entering the prove vstack status user EXEC command. You can remove a customer from the concur listing by entering the vstack on-hold-clients remove global configuration control.

Annotation ![]() When a client has been removed from the hold state to allow that client to join the network, you must restart the client to over again put it in the concord state (if the mode is manual) or to automatically upgrade if the manner is car and the join window is open.
When a client has been removed from the hold state to allow that client to join the network, you must restart the client to over again put it in the concord state (if the mode is manual) or to automatically upgrade if the manner is car and the join window is open.
When a new customer joins the network and the fashion is set up to auto, the join window state is active, whether or non the join window is open or closed. When the mode is prepare to manual and the join window is open up, the client is put on the hold listing. If the join window is closed, the client cannot bring together the network (denied).
Table ane-3 lists the join window states and the actions that are allowed or not allowed for each state.
| | | | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active | Immune | Immune | Allowed |
| Deny | Not immune | Allowed | Immune |
| Concord | Immune with user intervention | Allowed | Not allowed |
Starting with Cisco IOS Release 12.ii(58)SE,15.ane(1)SY, 15.0(ii)SE and later, 3.2(0)SE and later on, three.6.(0)Due east, and 15.two.(2)East, you lot tin manually change the bring together window country for a client or multiple clients from the denied land to the active or held state by using the vstack join-window-status index client-id { allowed | held } privileged EXEC control.
Updating Client Switches
Supported types of paradigm and configuration updates:
- Zero-impact update—For a client with no configuration. This could be for the initial installation of an paradigm and configuration on a new client, for image and configuration installation on a customer after a write erase and reload, or, in case of a replacement switch, if vstack fill-in is enabled. The Smart Install network must run DHCP to perform zero-impact updates.
On all clients, prior to Cisco IOS Release XE three.v.0E and Cisco IOS 15.2(1)SG, only image+config nix-touch on upgrades were supported. With Cisco IOS Release XE iii.6.0E and Cisco IOS Release 15.2(i)SG, image+config zero-touch upgrade are no longer mandatory; zero-impact config solitary and zero-affect image lonely upgrades are at present supported on all clients.
- On-demand update—For clients that are already in the network and continued to the manager. On-need updates can be performed on single customer or on all clients that belong to a built-in group. DHCP is not required for on-demand updates. The director needs the IP accost of a customer for a single-client update if the client is non in a congenital-in group. For an on-demand update of a customer running an epitome earlier than 12.2(52)SE, the client must have an enable password and an IP interface configured.
Y'all can practice nothing-touch or on-demand updates to any Smart Install client switches. Y'all tin besides use the vstack download-image and vstack download-config privileged EXEC commands from the director to update the image or configuration of any switch as long as the director has a connection (directly or through another switch) to the switch. Y'all can likewise telnet to a customer switch and employ the archive download-sw privileged EXEC command to update switch software. When yous telnet to a client switch, you lot must know the switch enable passwords to do any configuration.
Get-go with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(58)SE, fifteen.1(one)SY, fifteen.0(2)SE, 3.2(0)SE and later, 3.half dozen.(0)Eastward, you tin can perform a simultaneous update of multiple clients that take the aforementioned product ID and password by entering the alphabetize numbers from the director database in the vstack download-image privileged EXEC command.
Nada-Bear upon Installation
A zero-bear upon installation is an update initiated past the director on a client switch that has no configuration. You lot can perform a zero-touch installation on Smart Install capable switches and non-Smart Install switches. The zip-touch installation occurs automatically with little or no intervention. A switch with no configuration tin can be a new, out-of-box switch or 1 on which you take entered the write erase and reload privileged EXEC commands.
During a nothing-touch installation, do not impact the console keyboard or try to enter a command or auto return on the switch. Else, the auto install and Smart Install processes end. To recover and restart the process, you need to render to the organization prompt, enter write erase and reload commands, and restart the process.
During a zero-touch installation, the VLAN specified in the seed configuration for a particular client should be the aforementioned as the startup VLAN on the managing director. If it is not, the configuration backup procedure fails.
If the TFTP server is the director, the file is saved in the director root directory. If the server is another device, it is saved in the tftproot directory. This is the default directory in the TFTP server where the files to be sent using TFTP are stored. The imageclist file, the new configuration file, and the prototype are too stored in this directory.
Run across the "Configuring the TFTP Server" section.
Connecting to a Client Switch
To connect to the client switch control-line interface, enter the vstack attach { client-index | client_ip_address } privileged EXEC command. The customer-index number represents active clients in the Smart Install network, displayed in the command-line assistance by inbound a question marking (?) after the vstack attach command. The same client number is valid until the customer reboots.
To attach to a client, the client switch must be configured for telnet service and have a configured enable password.
Gear Head Wireless Keyboard Kb 3750 Software Download
DOWNLOAD HERE
Source: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/smart_install/configuration/guide/smart_install/concepts.html
Posted by: charliebuthrotimily.blogspot.com


Comments
Post a Comment